Circuit Diagrams
Series circuits
- In a series circuit, voltage is not the same in each part of the circuit.
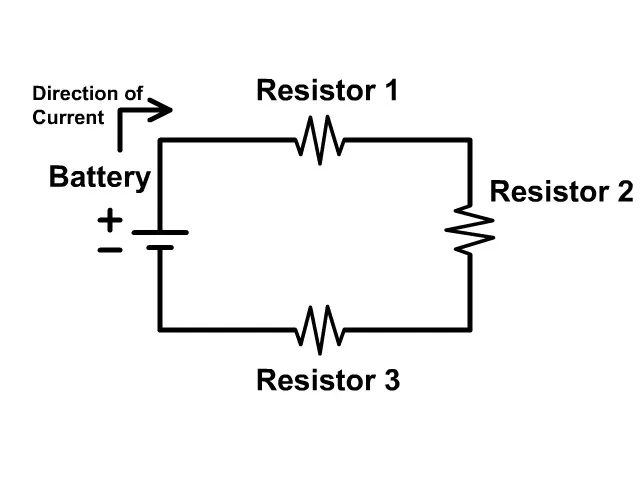
- \(V_{T}=V_{1}+V_{2}\)
- However the current is the same in all parts of the circuit.
- Resistance is defined as \(R_{T}=R_{1}+R_{2}\)
Parallel Circuits
- In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across the circuit, however the current is not the same.
- Current is given by the equation: \(I_{T}=I_{1}+I_{2}\)
- Resistance is inverted: \(\frac{1}{R_{T}}=\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}\)
- We can also use: \(R_{T}=\frac{R_{1}\times R_{2}}{R_{1}+R_{2}}\)
TIP: Restistors in parallel
- If two resistors are in parallel, and they have the same resistance, then you can just half the value of one of them.
- E.G. Two 2 ohm resistors in parallel give a total resistance of 1 ohm.
- E.G. Two 840 ohm resistors in parallel give a total resistance of 420 ohms.