Definitions, terminology and keys
Relational Databases and Database Keys
- To prevent data duplication, each record uses a primary key field, which is unique. It can be automatically generated.
- A primary key may be just numbers or a combination of letters and numbers.
- In the employee table, an employee number is unique for each employee and serves as the primary key.
- A relational database is a type of database that is structured and allows users to identify and access data which is in relation to other data.#
Relational database:
- A large set of data is distributed over various tables and connected using a relationship in a relational database. Hence, no redundant data.
- A relational database is efficient over flat-file databases as it is more efficient and takes up less space in memory.
Flat-file database:
- Presence of redundant data, that is, repetition of data in a database.
- Due to the presence of redundant data, more memory space is required and it is also less efficient.
- For example, a library may store information such as a book list, member list, department, book location, research paper list, staff details and many more.
- Storing these details in a single flat-file system would lead to more memory space requirement and data redundancy.
Entities:
- An entity is an object in a system for which the information is stored.
- A characteristic of an entity is its attribute.
- In a record, attributes about an entity are stored.
- For example, let us consider a book as an entity.
- Author, name of the publisher, year of publication, price of the book, and ISBN number are its attributes.
Foreign Keys:
- In a relational database, each table contains information about just one entity.
- Each table has a primary key and these tables are linked together using these primary keys and foreign keys.
- Foreign keys are a link to primary keys.

- A secondary key is an index of all primary keys. Let us assume some person calls library to find the availability of a book.
- He may not know the BookID so he will use the Title of the book to enquire about it.
- Use of secondary keys helps us to search quickly.
- Sometimes, more than one secondary key shall be used.
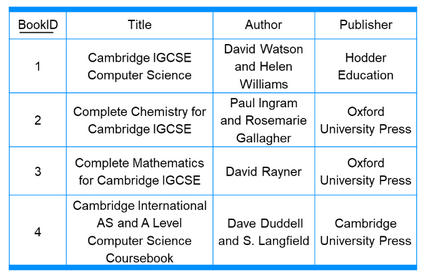
- Referential integrity ensures that all foreign keys represent a valid and existing primary key in its parent table.
- For example: In Books table, if you delete the record for BookID=2, it will create an orphaned record (shown in red colour) in Bookslent table.

Relationship between entities
Entities are related to each other using one of the following relationships:
- One to one
- One to many
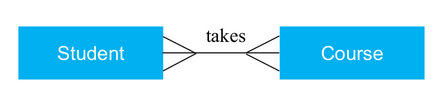
- Many to many
One to One:
- One entity is related to another entity only. For example: A person has one email address.

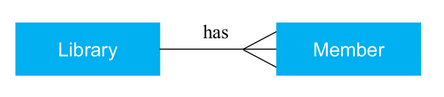
One to many:
- One entity is related to many entities. For example: A library has many members.
Many to many:
- Many entities are related to many entities. For example: Many students can take a course and a course can have many students.
Database:
- A database is an organised collection of data, which allows users to obtain and process information according to their requirements.
Structure of a database:
- Data in a database is stored in the form of tables.
Table:
- A table consists of various records. Each record consists of several fields.
Relational Database:
- A relational database is a type of database that is structured and allows users to identify and access data which is in relation to other data.
Entity:
- An entity is an object in a system for which the information is stored. In a relational database, each table contains information about just one entity.
Attribute:
- A characteristic of an entity is its attribute. In a record, attributes about an entity are stored.